Achievements of Ministry of Defence During the Year 2013 - PIB Report
Press Information Bureau
Government of India
Ministry of Defence
19-December, 2013 14:53 IST
Achievements of Ministry of Defence During the Year 2013
YEAR END REVIEW - 2013
Reaching
out to innumerable victims of the devastating flash floods &
landslides of Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh that struck on 16/17th
June by mounting the biggest ever Rescue & Relief operations in
these two States by the Indian Armed Forces was the most visible
achievement of the year. The eventful year also saw augmentation of
Nation’s defence preparedness by adding new weapon. In defence R&D,
successful test flight of 5000 Km range ICBM Agni-V, launching of
long-range cruise missile Nirbhoy and continued successful user trials
of Agni-II, Agni-III, Agni-IV, Prithvi-II, Supersonic BrahMos and Beyond
Visual Range missile “Astra” during the year displayed the nation’s
prowess and self-reliance in advanced missile technology development
programme.
The year also witnessed capacity
building in existing and new strategic areas through acquisitions and
development of new weapons / platforms which include commissioning of
India’s biggest aircraft carrier 44,500 tonne capacity INS Vikramaditya
on 16th November, preceded by the launching of India’s own IAC-INS
Vikrant and commissioning of deadly Mig-29K squadron into the Indian
Navy. Similarly, induction of first P-8I Boeing aircraft into the Navy
alongwith joining of C-17 Globemaster-III and Pilatus PC-7MKII aircraft
into the Indian Air Force consolidated our hold in different strategic,
logistics and training arena. The nuclear reactor fitted in the
indigenous nuclear powered submarine INS Arihant, in the making,
attaining criticality also pointed towards this end. The year gone by
also saw systematic force projection of our Armed Forces in India’s
neighborhood and far off Asian Region by engaging them through military
exercises and defence diplomacy, when Indian Navy perhaps undertook a
record number of exercises with foreign Navies to build Navy to Navy
co-operation, understanding and inter-operability. The Indian Army and
IAF also supplemented these efforts by undertaking a number of military
exercises with their friendly foreign counterparts. In this context our
prowess in fire powers, anti-terrorist operations and network centric
warfare were amply demonstrated by IAF exercises ‘Iron Fist’ and ‘Live
Wires’ and Army’s biggest war game exercises Indra and Indo-French
exercises ‘Shakti-2013’.
The nation achieved
spectacular progress in strengthening coastal security network,
ex-servicemen’s welfare, and its journey towards modernisation and
indigenization of Indian defence industry complex by adopting a policy
of ‘Swadeshi’ where transparency and accountability were the hallmarks.
Along
with these highs, there were some lows too. The sudden and unprovoked
attack from the Pakistan Army in the guise of armed infiltration in the
Line of Control in Poonch and later in Keran sector of J&K brought
disquiet into the region. Though our soldiers retaliated these recurrent
attacks with full force at their command, yet there was no stopping of
ceasefire violations from Pakistan side, which kept happening almost all
through the year. The thaw in India-China border relations was also
broken in April when Indian Army was once again challenged by China’s
Peoples’ Liberation Army (PLA) by their repeated incursions into Ladakh
Sector on the LAC. Thankfully after the face –off between the troops on
both sides for nearly one month, both sides simultaneously withdrew from
the contentious areas of LAC in this sector.
The
devastating fire accident in our frontline submarine INS Sindhurakshak
and it’s going down under the sea in Mumbai Naval Dockyard in August
this year was another big loss to the Indian Navy. The Board of Inquiry
instituted by the Government to find out the cause of this mishap
hopefully will look into all angles of the accident and suggest measures
so that the same is not repeated in the fighting arm of the Navy.
Reaching out to the People in Distress
A
cloud burst and torrential rain took thousands of tourists and pilgrims
by surprise in Uttarakhand & Himachal Pradesh in the third week of
June. Immediately, the Armed Forces were called by the state Government
of these two states for rescuing its citizens and tourists from some of
the most dangerous terrains devastated by floods & landslides.
Within no time, the Forces sprang into action and launched the biggest
rescue operation conducted by the defence and para-military forces
anywhere in the world. The troops from Central Command of the Army
launched the biggest rescue and relief operation ‘Rahat’ in
collaboration with ITBP, BRO and National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
on June 17. Sensing the gravity of the situation, IAF mobilised 54
transport aircrafts and helicopters for rescue efforts, which also
included stationing a gigantic strategic airlifter C-17 Super Hercules
in Jolly Grant, Dehradun airfield to evacuate the stranded tourists and
general people to safer places. Indian Navy also deployed its marine
commandos on 25th June, which with foot soldiers of the Army, rescued
hundreds of pilgrims and evacuated thousands to safer places.
Our
Armed Forces’ laudable role and conduct of operations to minimise the
effects of cyclone ‘Phailin’, which struck the Odisha & Andhra
Pradesh Coast in the fateful evening of 12th October also came for
universal praise and commendation from all quarters.
New Milestones in Defence R&D
Agni
–V: India reiterated its expertise in high end missile technology when
the second test flight of over 5000 Km Intermediate Range Ballistic
Missile (IRBM) Agni-V proved successful on 15th September. The missile
designed by the DRDO and launched from Wheeler Island off Odisha Coast
reached the pre-designed target point, over 5000 Km away, in the Indian
Ocean, incorporated many indigenous technologies. These include the
composite rocket motor, state-of-the-art avionics, 5th generation
on-board computer distributed architecture, highly accurate laser
Gyro-based Inertial Navigation System (RINS), reliable redundant
micro-navigation system and the re-entry kit shield that withstands
temperature of more than 4000 degrees Celsius ensuring that avionics
function smoothly by maintaining an inside temperature less than 50
degrees Celsius.
After successful test firing of
Agni-V, DRDO now aims for 10,000 Km range Inter –Continental Ballistic
Missile (ICBM), which according to its Chief would be preceded by above
6000 Km range Agni-VI to be launched soon.
In the
meantime the training and user trials of Agni-II, Agni-III and Agni-IV
of varying ranges as well as supersonic 300 Km range BrahMos and
Prithvi–II have been successfully accomplished in the year. All these
missiles which were tested by the users, the Strategic Forces Command of
Indian Army, in the presence of scientists and engineers of DRDO and
other collaborating laboratories.
LCA programme
finally out of woods: The much awaited and long-delayed indigenous Light
Combat Aircraft (LCA) project for the Indian Air Force undertaken by
the Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd. (HAL) with its tech partner DRDO finally
will see the light of the day, as its initial operational clearance-II
is scheduled on 20th December to be held at HAL, Bangalore.
The
LCA ‘Tejas’, a fourth generation fighter aircraft is meant to meet the
versatile and stringent requirements of the Indian Air Force as its
front-line multi mission aircraft. Besides developing the fighter
version, Aeronautics Development Agency (ADA), the main lab for DRDO
incharge of designing and making this metal bird, is also now fully
engaged in developing LCA Trainer for IAF and LCA Navy Trainer.
The
weaponisation programme, the focus of the current IOC phase of LAC
attained a significant milestone by the successful and flawless firing
of the air-to-air close combat missile, weapon carriage and release
trials. Recently, initial block of flight testing of LCA Naval variant
(NP-1) has been successfully completed. Successful Night Flying of LCA
has been yet another achievement. Thus the programme is moving towards
certification leading to Final Operational Clearance (FOC), which is
expected towards the end of next year.
INS Vikrant
Launched: India launched its first indigenous aircraft carrier INS
Vikrant on August 12 at Kochi marking the end of Phase-I (IAC-I) of the
project. The imposing ramp of the 37,500 tonner Short Take Off But
Assisted Recovery (STOBAR) carrier boasted indigenous design and built
capabilities of the country.
Atomic Reactor of
‘Arihant’ went critical: In adding another feather to its crown of
superior state-of-the-art nuclear technology, Indian defence scientists
and technologists successfully activated the atomic reactor on board INS
Arihant in early August. The next major milestone would be when Arihant
begins its trials, which has been planned for September 2014. The
nuclear submarine will go for extensive trials before it becomes
operational with the Indian Navy.
New Weaponary/Platforms to Strengthen Defence Preparedness
INS
Vikramaditya: India finally commissioned its second aircraft carrier
44,500 tonne INS Vikramaditya into the Indian Navy at the Sevmash
Shipyard in Severodvinsk in Russia on 16th November when Defence
Minister Shri AK Antony commissioned the carrier after its extensive
refurbishment and refit over the past few years. The Carrier, in its
previous avtar as Admiral Gorshkov, can carry over 30 combat
aircraft/helicopters and has the staying power of operating nearly 45
days in high seas with its 1600 crew & officers. It is equipped with
long range Air Surveillance Radars, Advanced electronic warfare suite
capable of maintaining a surveillance bubble of over 500 Kms around it.
The deadly Mig -29K deep penetration striker aircraft, Kamov-31, Sea
Harriers and ALH Dhruv helicopters comprise its air element. The ship is
also equipped with the state-of-the-art launch and recovery system
along with aids to enable smooth and efficient operation of sea-borne
aircraft. The carrier which is now sailing towards India is expected to
arrive in mid February 2014 and will be based at Karwar Naval Base in
the Western Coast.
C-17 Globemaster III
Giving
impetus to the long standing strategic airlift of the Indian Air Force,
the Boeing C-17 Globemaster III was formally inducted into the IAF on
02 September at Hindon Airbase near Delhi. Four of the C-17 have been
already delivered to the IAF and the fifth aircraft joined the fleet in
November.
Pilatus PC 7 MK II Basic Trainer Inducted
The
IAF’s premier flying Academy located at Dundigal, Hyderabad witnessed
the unveiling of Pilatus PC7MKII basic trainer aircraft, which heralded a
new era in imparting high quality flying training to budding pilots
ensuring proficiency in handling more sophisticated aircraft.
Boeing P-8I Arrives at INS Rajali
The
first of the three Boeing P-8I aircraft for the Indian Navy arrived at
INS Rajali, Arakonam on 15th May. The P-8I aircraft based on the Boeing
737-800(NG) airframes is equipped with an array of sensors for maritime
reconnaissance, anti-submarine operations and for electronic
intelligence missions. The aircraft has drawn its lethality from its
arsenal of highly potent Anti-Surface and Anti-Submarine weapons.
Advanced Jet Trainers (AJT) inducted
The
Indian Navy inducted the first fully Indian manufactured Hawk Advanced
Jet Trainer (AJT) at INS Dega, Vishakhapatnam on 06 November.
ALH–Dhruv Squadron Commissioned
The first Advanced Light Helicopter (Dhruv) Squadron was commissioned into the Navy at Kochi on 12 November.
Mig -29K Squadron Commissioned
INAS
303, the first Mig 29K squadron was commissioned on 11th May 2013 by
the Defence Minister Shri AK Antony at INSA Hansa, Goa. Mig-29K,
arguably one of the best in the subcontinent today is equipped with
high-end avionics completed with anti-aircraft beyond visual range
missiles, guided anti-ship missile and smart guided bombs and rockets.
Launching of GSAT-7 satellite
Launching
of GSAT-7, a dedicated communication satellite for the Indian Navy on
30 August gave a boost to realization of Navy’s network centric war
capability based on an indigenous platform. With multiple transponders
in various frequency bands, the satellite will provide voice and data
communication and hence will help in seamless integration among the
various command centres and Naval Units operating across the IOR.
INS Sarayu Commissioned
INS
Sarayu, the lead ship of the indigenous Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel
(NOPV) Project was commissioned on 21 January. Aimed at meeting the
increasing ocean surveillance and patrolling requirements of the Indian
Navy, the primary role of the ship is to undertake EEZ surveillance,
anti-piracy patrols, fleet support operations and provide maritime
security to offshore assets and carry out escort operations for high
value assets.
INS Trikand Commissioned
INS
Trikand, the last of the three ‘follow on Talwar class’ frigates was
commissioned into the Indian Navy at Kaliningrad, Russia on 29 June. It
carries a state-of-the-art combat suite which includes the supersonic
BrahMos Missile system, advanced surface-to-air missile, upgraded A190
medium range gun, Electro-optical 30mm close-in weapon system and
Anti-submarine weapons and an advanced electronic warfare system. Her
sister ships INS Teg and INS Tarkash were commissioned last year.
IAF- launches its 3G WCDMA Cellular Network Project
The
Indian Air Force launched its 3G Cellular Network named AFCEL (Air
Force Cellular) recently, thereby, becoming the first in the Services to
have commissioned its own captive 3G network. Launching of phase-I of
AFCEL in the National Capital Region is a milestone in the IAF’s
transformation into a modern, networked aerospace entity with full
spectrum dominance. With this project IAF has taken a quantum leap
forward to their quest to provide mobile and secure entry-point
connectivity to the air warriors deployed across the length and breadth
of the country as it will facilitate real time exchange of information
in an ever dynamic operational environment.
International Co-operation through Exercises & Defence Co-op. Talks
During
the year, the Indian Army, to develop Army to Army understanding and
inter-operability, conducted bilateral exercises with China, France, UK,
Russia and Nepal. India-China joint exercises Hand-in-Hand 2013
conducted in Chengdu Province of China culminated on 13 Nov. This
battalion level exercise practiced the joint operations on Cordon &
Search in international scenario. Exercise ‘Ajeya Warrior’, a four week
Indo-UK joint military exercise, also aimed at enhancing counter
terrorism skills. In October Indian and Russian armies conducted a joint
exercise, Indra, at Mahajan field firing range in Thar Desert of
Rajasthan. The event saw both sides perform various combat exercises
including anti-terrorist operations. It also saw a joint Indo-Russian
command planning. A joint exercise between India and the French armies
was organised from September 9-20 in the French Alps at Grenoble.
As
friendly neighbours, an Indo-Nepal battalion level joint military
exercise, Surya Kiran-V was conducted at Pithoragarh in Uttarakhand from
23 September - 06 October.
Based on the agreement
during the 7th Nepal-India Bilateral Consultative Group on Security the
two countries commenced joint training at platoon level in 2011. The
first two joint exercises focused primarily on jungle warfare and
counter-insurgency operation. Troops shared their experiences and
exhibited skill sets during training at Counter-Insurgency and Jungle
Warfare School at Vairangate in Mizoram and a similar school at
Amlekhganj in Nepal. Later, the joint training was upgraded to company
level in 2012 and based on experiences gained in previous two exercises,
it was further upgraded to battalion level this year.
In
a bid to further strengthen the existing Indo-French relationship, a
joint exercise between India and the French Army called ‘Shakti – 2013’
was organised from 9 – 20 September at Jodhpur which is the second joint
military exercise between the two countries.
This
platoon level exercise’s theme was on counter-insurgency operations in
high altitude mountainous terrain under the UN Charter, thus emphasizing
the shared concern of both countries about global terrorism. An added
aim of the exercise is to qualitatively acknowledge of each other’s
military procedures, thus increasing the scope for inter-operability and
better responsiveness to a common threat.
Record Exercises with Foreign Navies
In
its endeavour to build Navy to Navy co-operation, understanding and
inter-operability, the Indian Navy held military exercises with Navies
of numerous friendly countries. These included:
- CORPAT
– These Co-ordinated Patrols (CORPAT) with maritime neighbours of India
not only strengthened naval co-operation with our neighbours but also
helped in developing trust and confidence among participant countries.
- First
India –Myanmar Navy Co-ordinated Patrol in March 13 with the aim of
flushing out extremists operating from Myanmar soil and Navy-to-Navy
understanding was successfully conducted.
- Indo-Thai bilateral naval exercise in April and November.
- India-Indonesia bilateral naval exercise in May and September.
- India-RSN (Republic of Singapore Navy) exercise SIMBEX in May.
- Bilateral naval exercise ‘Naseem Al Bahar’ between India and Royal Navy of Oman on 11 September.
- Indo-UK exercise ‘Konkan’ in October.
- Indo-US naval exercise ‘Malabar’ in November.
- India-Sri Lankan Navy exercise ‘SLINEX’ in November.
- Naval exercise between India and Japan Maritime Self Defence Forces in December.
- India-Brazil-South
Africa Maritime Exercise ‘IBSA mar’ was conducted among Indian,
Brazilian and South African Navies in the IOR. The exercise is the
maritime element of the regional co-operation initiative among these
three countries.
Exercise on the anvil
The
13th Meeting of India-Russia Inter-Governmental Commission on Military
and Technical Co-operation (IRIGC-MTC) was held at Moscow in November
co-chaired by the Defence Minister Shri AK Antony with his Russian
counterpart Mr. Sergey Shiogu. The meeting which gave a new impetus to
the relationship decided that the two countries will hold joint
Air-Force level exercises, for the first time besides a joint Navy
exercise in the Peter the Great Bay in the Sea of Japan, both in 2014.
IAF under Transformation
As
the Indian Air Force (IAF) celebrates its 81st anniversary, it is
conscious of the transformation it has been undergoing since 1995 where
it wrote its first war doctrine, purchased Sukhoi-30 aircraft from
Russia, raised the pitch for aerospace command and formally shed its
tactical role for a strategic one.
Keeping in view the
rapidly changing geo-political situation and to fulfil its new
operational stance, the IAF has taken a number of steps related to its
force level, infrastructure development, force multipliers, training and
most importantly its mindset from a tactical to a strategic entity.
Besides
inducting AWACS and AEW&C for better early warning and assured air
defence, net centricity for better command, control, communications,
computers and intelligence gathering, better strategic lift capabilities
and advanced electronic warfare, are now the buzz words in the IAF.
In
addition to tying up with Russia to develop and manufacture
state-of-the-art 5th Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA), India has also
collaborated with Russia for development of a multi-role transport
aircraft. The design preparation and allied works relating to FGFA has
picked up the momentum after satisfactory high level defence talks with
Russia which was held in Moscow in November. Besides these, IAF has
planned to upgrade select Mig-21 Bis, Mig-27, Mig-29, Mirage-2000 and
Jaguar fleets and has taken steps to further compress the delivery
schedule of HAL Built Su-30 MK-II, besides 40 more acquired from Russia.
Developing Strategic Partnership
Working
in tune with its ‘Look East Policy’, India has started forging
strategic partnership with countries of Far East and ASEAN. In this
context, India’s willingness to co-operate with Vietnam Republic in
helping it exploring oil from the South China Sea is significant.
Similarly its relations with Japan, South Korea, Thailand, Malaysia,
Indonesia, Maldives, Nepal and Afghanistan is steadily growing through
bi-lateral exercises and fruitful defence co-operation talks in the form
of defence exchanges, training and other areas.
India’s
bilateral defence ties with US, UK, France, Turkey, Australia, Brazil,
South Africa, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Iran, Germany,
Russia, Saudi Arabia, Israel, Oman etc. is growing over the years.
Indo-French High Committee on Defence Co-operation which met in October
this year decided to further strength the ties in different fields which
include joint research & development in high technology and
transfer of technology, defence equipment collaboration, training and
close navy-to-navy interaction in matters like joint exercises and
defence exchanges. Already France is committed to manufacture and
handover of three state-of-the-art lethal Scorpene submarines and
another three will be built at Mazagon Dock Ltd, Mumbai with active
French collaboration and TOT.
Coastal Security Initiatives
Drawing
lessons from 26/11 terrorist attacks on Mumbai in 2008, the Govt. took a
number of security measures to close the gaps in India’s vast coastline
and strengthen the coastal security apparatus in a planned manner by
involving all stakeholders in this endeavour. Under Phase-I of the
Coastal Surveillance Network Project installation of 36 radar chain to
have a gap free Coastal Surveillance Network (CSN) was envisaged. In the
first Phase of the project, the coastal States/UTs were provided with
73 coastal police stations, 97 Check Posts, 58 Out Posts, 30 Barracks,
204 boats, 153 jeeps and 312 motorcycles.
The
completion of the phase-I of the project at a cost of Rs. 646 crores on
the Indian mainland took place when MoS, Defence, Mr Jitendra Singh
inaugurated the static sensor chain at Visakhapatnam on 23 November.
India has already a chain of 36 radars along the Maharashtra, Gujarat
and Kerala coast.
In the phase-II of CSN which
will cost Rs. 1580 crores, we will have another 38 radars chain to cover
the rest of the 7,500 Km long coastline. The Indian Coast Guard was
delegated to implement the project. For this, the Govt. had signed the
contract with the state owned Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) in Sept 2011
at a cost of Rs 602 crores considering the strategic nature of the
turnkey project and with an aim to develop indigenous capabilities.
Under this scheme, the coastal States/UTs interalia are provided with
131 coastal police stations, 10 Marine Operation Police Centres (MOCPs),
60 jetties, 225 boats of various categories and a lump sum assistance
of Rs. 15 lakhs per coastal police station to develop its
infrastructure.
Linking up the National Automatic
Identification System Network (AIS) and Vessel Traffic System (VTS) off
Gulf of Khambat with the Coastal Security Network would help the
security forces in identifying a friend or foe in the Indian waters.
Of
late, a worrisome trend is the problem of tackling the issue of Private
Armed Security Guards on board Commercial ships in international waters
as well as territorial waters. The urgent need to regulate these
‘floating armouries’ has assumed significance in the backdrop of two
recent incidents close to Indian Coast. A high level meeting on Coastal
Security convened at Delhi by the MoD recently decided to take up this
issue of Private Armed Security Guards with international fora such as
International Maritime Organisation (IMO).
Welfare of Jawans & Ex-Servicemen
Welfare
and all-round well being of ex-servicemen and war widows have been the
cornerstone of our rehabilitation policy since independence.
In
our ongoing effort to improve the well being of jawans, the govt has
further widened the scope of ECHS (Employees Contributed Health Scheme)
and established more polyclinics and regional health centres. To improve
the living and working conditions of jawans, several steps have been
taken to improve the quality of rations, accommodations and clothing.
For soldiers deployed in high altitude areas, warm clothings, special
shoes and attractive monthly compensatory allowances have been provided.
To protect the officers, jawans and other ranks posted in very high
altitudes from mental and physical fatigue, liberal leave facilities as
well as rotation of personnel at regular intervals have been given high
priority. To reduce the stress levels of jawans so as to avoid stray
cases of fragging and fratricide, Counselling Centres have been
established at different levels manned by professional psychologists and
psychiatrists starting from unit to command level.
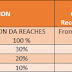
MAP:-
To overcome the acute shortage of accommodation for serving defence
personnel, Married Accommodation Project (MAP) was started by the Govt.
in 2002. In this project, totalling two lakh dwelling units (DUs) were
supposed to have been constructed. After implementation of Phase-I of
the project, approximately 60,000 dwelling units have been constructed.
This has enhanced the satisfaction level with regard to availability of
married accommodation to 60%. In the second phase of MAP, construction
of about 68,400 DUs is going on at different places and on their
completion, satisfaction level will increase to 72%. In addition,
construction of 71,000 DUs of Phase-III is now under planning. On
completion of all the phases of the project, the satisfaction levels
will reach 85%.
For ex-servicemen welfare, Govt.
has taken a number of steps to further improve their pension. For this, a
high level committee was constituted by the Govt. in 2012 to look after
the pay and pension anomalies of armed forces personnel and family
pensions etc. Acting upon the recommendations of the committee, the
Govt. further liberalised the pension amount for different types of
ex-servicemen pensioners last year which costs the exchequer of
approximately Rs 2200 crores.
OTHER IMPORTANT EVENTS/PROGRAMMES
1.
To give further encouragement to promote indigenisation and
developing Indian defence industrial base in the country, the Government
promulgated amended Defence Procurement Procedure 2013 on 01 June,
where a number of concessions and priorities have been given to ‘Buy
Indian’ and ‘Buy and Make’ (Indian) categories, besides bringing
further clarity in the definition of the Indigenous Content and
simplifying the Buy and Make (Indian) process. Other significant changes
include incorporation of the new offset policy guidelines which were
promulgated in August 2012 and revision of the chapter on Ship-building
which had been introduced in the DPP 2011. The Ministry has also
undertaken the exercise of further simplification of the Make procedures
and revision of the Fast Track Procedures which is likely to be
completed in the near future.
2. Indian Air Force
formally bade farewell to its Mig-21 (FL) fleet, after the fleet’s
glorious service to the nation for more than thirty years, in December
this year. Their place will be filed up by the LCA fighter version in
near future.
3. India signed the much awaited Border
Defence Cooperation Agreement (BDC) with China during the Prime Minister
Dr. Manmohan Singh’s visit to China in October. The agreement is
expected to bring in a relatively peaceful and intrusion free LAC in the
northern sector. The agreement lays out a protocol to prevent incidents
like intrusion, when Chinese troops came and pitched tents inside
Indian territories in August/September.
4. On July 02,
2013, India unveiled the much awaited National Cyber Security Policy to
create a secure cyber eco-system in the country.
5.
Indian Coast Guard Ship ‘Rajdoot’, the sixth in the series of light
Inshore Patrol Vessels (IPVs) designed and built by M/s Garden Reach
Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata was commissioned at Kolkata
in May 2013.
6. The Naresh Chandra Task Force
constituted by the Govt. on national security and higher defence
management submitted its recommendations, where among others, it has
recommended to create the post of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) in the
Indian Armed Forces.
7. The first NCC National Games was
held in Delhi in November where 1900 boys and girls athletes from 17 NCC
directorates, from all the States and Union Territories took part. The
eight day long Games was inaugurated by the DG, NCC Lt. Gen P.S. Bhalla
amidst much grandeur and fanfare.
8. The foundation stone
for India’s first National Defence University (INDU) was laid by the
Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh in Binola, near Gurgaon in May 23,
2013 in the presence of high dignitaries including the Defence Minister.
9. INAS ‘HANSA’ in Goa celebrated its diamond jubilee on 11th May, 2013.
10. First Passing Out Parade at the newly established Indian Naval Academy at Ezhimala in Kerala was held on 25th May, 2013.
11. Indian Coast Guard’s Offshore Patrol Vessel (OPV) ICGS ‘VAIBHAV’ was commissioned on May 21, 2013.
12.
Defence Minister Shri AK Antony dedicated to the Nation the new Air
Force Station at Thanjavur in Tamil Nadu on 27th May 2013 where a
special runway has been made for the operation of Su-30 MK-I fighter
aircraft.
13. Defence Minister visited Maldives in April 2013.
14. Defence Minister visited Myanmar on January 21, 2013.
15. Commissioning of Indian Coast Guard Ship Rajkamal was held in 08 January 2013.
16. Govt. orders a CBI probe into Augusta Westland Contract for 12 VVIP Helicopters on 12 February 2013.
17.
The 9th edition of Asia’s biggest air show ‘Aero-India’ -2013 took
place in Bangalore in February 2013, where 44 countries took part.
Defence Minister Shri AK Antony inaugurated this mega event where in the
Air show vintage Tiger Moth aircraft made its flight appearance after a
gap of 22 years.
18. HAL formally handed over to Army the weaponised edition of ALH-Dhruv as ‘ALH MK-IV Rudra’ on 08 February 2013 at Bangalore.
19. Commissioning of Indian Coast Guard Ship ‘Rajratan’ held on 11 February 2013.
20.
Chinese Defence Minister with a delegation visited India on 22nd March
2013 and India-China Talks on Defence co-operation held in Delhi.
21. Indian Navy concludes theatre level exercise Tropex-13 on 02 March 2013.
Source: PIB News