Railway Employees Retirement Benefits – Pension (Applicable to Railway Employees who have been appointed on or before 31.12.2003)
1. What is Pension?
Pension is a lifelong Retirement Benefit, paid monthly to a Railway Servant on retirement from service.
The pension scheme was introduced in 1957 was,
however, made compulsory for all the employees appointed on and after
16.11.1957 in Railway Service.
2. Who are eligible for pension?
(a) All those Railway Employees, who were
appointed on or after 16.11.1957 (up to 31.12.2003) are compulsorily
governed by Pension Scheme.
(b) The employees who were in service
on 1st April, 1957 or were appointed during the period from 1st April,
1957 to 15th November, 1957 were required to exercise an option to elect
for Pension Scheme by 31.03.1958. These options were subsequently
extended from time to time.
3. What are the different kinds of Pension?
Pensions are divided into the following four classes:
(i) Compensation Pension
Compensation Pension means the pension granted to a
Railway Servant who is discharged from Railway service due to abolition
of a permanent post.
(ii) Invalid Pension
Invalid Pension means the Pension granted to a
Railway Servant who retires from service on suffering from contagious
disease or a physical disability, which affects the efficient discharge
of his duties.
(iii) Superannuation Pension
Superannuation Pension means the Pension granted to a Railway Servant who retires on attaining the age of 60 years.
4. What are Basic Conditions for Earning Pension?
Entitlement to pension commences on completion of 10
years qualifying service. A Railway Servant, who has completed less
than 10 years’ qualifying service, is entitled to a service gratuity
only.
5. What is the New Pension Scheme?
The Government of India has introduced a New Pension
Scheme (Defined Contributory Pension System) replacing the existing
system of Defined Benefit Pension System. The New Scheme is applicable
to new entrants to Government service w.e.f. 01.01.2004. Under Tier-I of
the system, Government servants shall compulsorily make a contribution
at the rate of 10% of salary and a matching contribution will be made by
the Government.
Tier-II is a withdrawable and
Non-Pensionable Account and will have the system of Voluntary
contribution. The contributions will be kept in a separate account and
will be withdrawable at the option of the Government servant. Government
will not make any contribution to Tier-II Account. This is not
operative at present.
6. What is the formula for determining the Amount of Pension?
With effect from 01.01.2006, Pension is calculated
as 50% of 10 months Average Emoluments or 50% of Last Pay Drawn
whichever is beneficial to the employee subject to a minimum
of Rs.3500/- per month.
Note: If the amount of pension contains a fraction of a Rupee, the amount will be rounded off to the next higher rupee.
7. What are Average Emoluments?
(i) The terms “Average Emoluments” is
determined with reference to Basic Pay drawn by a Railway Servant during
the last ten months of his service.
(ii) If during the last 10 months of service,
a Railway Servant is absent from duty or on extra ordinary leave
(without leave salary) or has been under suspension, the aforesaid
period of leave or suspension is disregarded in the calculation of the
average emoluments and an equal period prior to ten months is
considered.
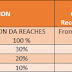
8. What is the additional quantum of Pension available to benefit old aged Pensioners?
The quantum of pension available to old aged Pensioners shall be increased as under:
| Age of Pensioner |
Additional Quantum of Pension
|
| From 80 years to less than 85 years |
20% of revised Basic Pension
|
| From 85 years to less than 90 years |
30% of revised Basic Pension
|
| From 90 years to less than 95 years |
40% of revised Basic Pension
|
| From 95 years to less than 100 years |
50% of revised Basic Pension
|
| 100 years or more |
100% of revised Basic Pension
|
9. What is the Pension Benefit admissible to different types of Railway Employees?
The Pension Benefits granted to Railway Employees, in different cases are:
(i) Permanent Railway Employees
(a) Qualifying service of less than 10 years
No pension but service gratuity shall be paid at a
uniform rate of half months emoluments for every completed six monthly
period of qualifying service.
(b) Qualifying service of 10 years or more shall entitle an employee to get pension subject to a minimum of Rs.3500/- per month.
(ii) Temporary Railway Employees
(a)Temporary employees retiring at the age of
superannuation or on being declared permanently incapacitated for
further service by the appropriate medical authority after rendering
service of not less than 10 years will be paid Retirement Benefits at
the same scale as is paid to the permanent employees.
(b)A temporary employee’s family, who dies in
harness, will be allowed the same death benefits as are admissible to
the family of permanent employees.
(iii)Employees who are removed or dismissed from Railway Service
No pensionary benefits are granted to Railway
Servant on whom the penalty of removal or dismissal from service is
imposed. However, in case of a Railway Servant so removed or dismissed,
the authority who removed or dismissed him from service may award
‘Compassionate grant’ corresponding to ordinary gratuity and/or DCRG
and/or allowances corresponding to ordinary pension, when he is
deserving on special consideration, provided that the compassionate
grant and/or allowances awarded to such employee shall not exceed two
thirds of apensionary benefits which would have been admissible to him
if he had retired on medical grounds.
10. Through which authorities/offices can Pension be drawn?
Pension can be drawn through Post Offices, Treasuries or Nationalised Banks.
11. What are the conditions for disbursement of Pension?
Disbursement of Pension depends on furnishing of a
non-employment or an employment/ re-employment certificate by Pensioner
once in a year in the month of November each year in the prescribed form
to the Pension Disbursing Authority. Similarly, besides non-employment
certificate, a ‘Life Certificate’ duly signed by a Gazetted Officer or
by some other well known and trustworthy person is also required to be
furnished. Until the said certificates are furnished, Pension for the
subsequent months will not be disbursed.
QUALIFYING SERVICE
1. What is qualifying service?
Qualifying service is the number of completed six
monthly periods of service which is taken into account for determining
the amount of pensionarybenefits.
Broadly, all periods spent on duty (including
Foreign Service for which contribution is paid to the Government) or on
leave including leave on medical certificate are allowed to be counted
for pension. The competent authority has discretion to allow extra
ordinary leave to count for pension
The service and periods rendered in the following
capacity are termed as ‘Qualifying Service’ and qualifying
for pensionary benefits:
(i) Continuous service on Indian (Government) Railways.
(ii) Continuous service rendered on
ex-company/ex-State Railway, taken over by the Government and followed
by service in Indian (Government) Railways.
(iii) Military/War Service rendered before joining
the Railways in terms of Rule 22, 34 & 35 of Railway Service
(Pension) Rules, 1993.
(iv) Service rendered under Central or State Government before transfer to Railways.
(v) Period of training followed by absorption against regular post.
(vi) Deputation period out of India on duty.
(vii) Authorised ‘Joining Time’.
(viii) Foreign Service rendered by a Railway Servant
shall count as qualifying service provided that contribution towards
cost of pensionary benefits of the Railway Servant, has been paid
either by the foreign employer or a Railway Servant himself, in respect
of entire period of Foreign Service.
(ix) All periods of leave with leave salary taken up to the date of superannuation.
(x) Extra-ordinary Leave (EOL)
(a) Extra-ordinary Leave taken on medical grounds
(b) If taken to join or re-join duty due to Civil Commotion or Natural Calamity, if he has no other type of leave.
(c) For higher scientific and technical studies.
(xi) Period spent on suspension
Time passed under suspension pending inquiry into
conduct, counts in full if on conclusion of enquiry, the Railway Servant
has been fully exonerated or the suspension is held to have been
unjustified. In other cases the period of suspension will only count if
the authority who reinstated him in service expressly declared to count
towards pensionary benefits.
(xii) Service rendered in casual capacity
Half of service rendered in casual capacity after
attaining temporary status will count for pensionary benefits on
absorption against a regular post.
For calculation of the length of qualifying service,
a fraction of a year equal to 3 months or more shall be treated as
completed one half year period.
2. What is the formula for calculating Qualifying Service?
(i) The fraction of a year in the qualifying service shall be reckoned in the following manner:
Fraction of a year
|
Number of completed
Six-monthly periods (half year)
|
| Less than 3 months |
NIL
|
| 3 months and above and less than 9 months |
01 (one)
|
| 9 months and above |
02 (two)
|
(ii) Qualifying service of 9 years and 9
months and above (up to 10 years) at the time of retirement shall be
treated as ten years of service.
(iii) After completion of minimum 20 years of qualifying service voluntary retirement can be taken.
(iv) Where the authority reinstating the
Railway Servant had not passed orders as to the treatment of period of
suspension for the purpose of Qualifying Service
for pensionary benefits, the period of suspension shall only be counted
if it had been treated as duty or leave due as the case may be.
Illustration for calculating Railway Pension:
In case of an employee serving in Pay Band-2
ScaleRs.9300-34800 in Grade Pay Rs.4200 who was drawing Last
Pay Rs.20000/- retires on superannuation after completing 33 years of
qualifying service. 40% commutation of Pension opted.
Pension
(Minimum Rs.3500/-)
|
= 50% of LP + DR |
= 50% of 20000
= Rs.10000/- + DR
|