Ministry of Labour & Employment
Building and Other Construction Workers Welfare Cess
17 DEC 2018
Pursuant
to the directions of Hon'ble Supreme Court contained in its judgement
dated 19.03.2018 in W.P. (C) No. 318/2006, the Central Government has
formulated a model welfare scheme for BOC workers which, inter alia,
envisages following maternity benefit, out of the BOCW welfare cess
fund, for those BOC workers who are not covered under Ayushman Bharat:-
(i) Paid maternity leave to registered construction workers ranging from 90 days to 26 weeks for up to two deliveries.
(ii)
Rs.6000/-per delivery for up to two deliveries to the wife of the
registered construction workers, which will be in addition to any other
benefit received from any Government Scheme in this regard.
The
Building and Other Construction Workers (Regulation of Employment and
Conditions of Service) Act, 1996 provides safety, health and welfare
measures for the building and other construction workers. For the
purposes of the above said Act, a cess is levied and collected at the
rate of 1% of the cost of construction by the State Governments under
the Building and Other Construction Workers’ Welfare Cess Act, 1996. The
States, through their respective State Building and Other Construction
Workers Welfare Boards, constituted under BOCW Act, utilize the cess
fund in terms of Section 22 of BOCW Act, 1996. The States and Union
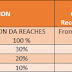
Territories have collected around Rs. 45473.1 Crore and have spent an
amount Rs. 17591.592 Crore upto 30.9.18.
The Welfare Schemes
funded from BOCW welfare cess fund are exclusively for the building and
other construction workers. Diversion of the cess fund for welfare of
other category of workers is not permissible under the BOCW (RECS) Act,
1996.
Utilization of Cess Fund under Section 22 of the Building
and Other Construction Workers (RECS) Act, 1996 Act and the registration
of building and other construction workers as beneficiary under section
12 of the said Act is done by the State Building and Other Construction
Workers Welfare Boards.
Besides the above, the Government is
implementing various Acts and Schemes to provide social security and
welfare benefits to workers, both in the organised and unorganised
sector. The social security to the workers in the organized sector is
provided mainly through five Central Acts, namely, the Employees' State
Insurance Act, 1948, the Employees’ Provident Funds & Miscellaneous
Provisions Act, 1952, the Employee’s Compensation Act, 1923, the
Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 and the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972.
In
order to provide social security benefits to the workers in the
unorganised sector, the Central Government is implementing Unorganised
Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008, to provide welfare schemes in
matters relating to life and disability cover, health and maternity
benefits, old age protection to the unorganised workers. Various
Ministries/Departments of the Central Government are implementing such
social security schemes like Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension
Scheme (Ministry of Rural Development); National Family Benefit Scheme
(Ministry of Rural Development); health and maternity schemes (Ministry
of Health and Family Welfare). The Central Government has also converged
the social security scheme of Aam Aadmi Bima Yojana (AABY) with Pradhan
Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) and Pradhan Mantri Suraksha
Bima Yojana (PMSBY) to provide life and disability coverage to the
unorganised workers depending upon their eligibility. These converged
schemes give coverage of Rs.2 lakhs on death at premium of Rs.330/- per
annum and coverage of Rs.2 lakhs on accidental death at premium of Rs.12
per annum, besides disability benefits as per the scheme. The annual
premium is shared on 50:50 basis by the Central Government and the State
Governments. These schemes are implemented and monitored by Life
Insurance Corporation of India and the concerned State Governments.
This
information was given by Shri Santosh Kumar Gangwar Union Minister of
State (I/C) for Labour and Employment in written reply to a question in
Lok Sabha today.
PIB