Recognition of Trade Unions – New Rule Proposed by the Govt – Has to have at least 66% Support of the Workers
Recognition of Trade Unions – In case no union garners the prescribed majority, the Bill provides for the formation of a collective bargaining council.
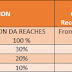
Soon, managements of companies will have to recognise trade unions that has the support of at least two-thirds or 66 per cent of workers, if the proposed Industrial Relations Code is enacted. Currently, there are no norms for recognising unions.
A union proving the requisite amount of support will also be considered as the representative body of workers to engage in dialogue with the management in case of a dispute. The revised Bill, containing this provision, has been sent for approval to the law ministry by the labour ministry.
In case no union garners the prescribed majority, the Bill provides for the formation of a collective bargaining council, where different unions will send their representatives. In such a case, a union gets a seat on the council for every 10 per cent of votes. Unions that do not get at least 10 per cent votes would not be included in the council.
Currently, there is no law that makes it mandatory for managements to recognise a trade union. Although there is a fundamental right to form unions and a statutory right to get it registered, there is no corresponding legal obligation on the employer to recognise a trade union, whether registered or not, even if they truly are representative.
“Recognition of a trade union is very different from registration. There have been numerous cases before tribunals where the management has refused to recognise a union as the bargaining body of workers. This provision will benefit both employers and workers as this will ensure a smooth dialogue process,” said a senior labour ministry official.
According to another ministry official, trade unions had objected to the original proposal of allowing a union that has even a per cent of votes higher than the second largest union as the sole negotiating agent during tripartite negotiations. For instance, in a situation where one union gets 41 per cent vote and the other 40 per cent, the second largest union with 40 per cent would have become irrelevant.
“They felt that it would have rendered a union with 40 per cent support useless and render smaller unions without bargaining power,” the official said.
Source: BS
Recognition of Trade Unions – In case no union garners the prescribed majority, the Bill provides for the formation of a collective bargaining council.
Soon, managements of companies will have to recognise trade unions that has the support of at least two-thirds or 66 per cent of workers, if the proposed Industrial Relations Code is enacted. Currently, there are no norms for recognising unions.
A union proving the requisite amount of support will also be considered as the representative body of workers to engage in dialogue with the management in case of a dispute. The revised Bill, containing this provision, has been sent for approval to the law ministry by the labour ministry.
In case no union garners the prescribed majority, the Bill provides for the formation of a collective bargaining council, where different unions will send their representatives. In such a case, a union gets a seat on the council for every 10 per cent of votes. Unions that do not get at least 10 per cent votes would not be included in the council.
Currently, there is no law that makes it mandatory for managements to recognise a trade union. Although there is a fundamental right to form unions and a statutory right to get it registered, there is no corresponding legal obligation on the employer to recognise a trade union, whether registered or not, even if they truly are representative.
“Recognition of a trade union is very different from registration. There have been numerous cases before tribunals where the management has refused to recognise a union as the bargaining body of workers. This provision will benefit both employers and workers as this will ensure a smooth dialogue process,” said a senior labour ministry official.
According to another ministry official, trade unions had objected to the original proposal of allowing a union that has even a per cent of votes higher than the second largest union as the sole negotiating agent during tripartite negotiations. For instance, in a situation where one union gets 41 per cent vote and the other 40 per cent, the second largest union with 40 per cent would have become irrelevant.
“They felt that it would have rendered a union with 40 per cent support useless and render smaller unions without bargaining power,” the official said.
Source: BS