The Payment of Wages Act 1936
The payment of Wages Act, 1936 is an important piece of legislation which regulates the payment of wages to employees in the industrial and other establishments, who are in respect of wages with average upto Rs.1600/- per month. It seeks to ensure timely payment of wages without any unauthorised deductions.
The payment of wages (Railways) Rules, 1936, as amended from time to time, were framed by the Central Government to secure proper enforcement of the provisions of the Payment Of Wages Act in respect of persons employed in railway including railway contractors who employ 20 or more persons on any day in the preceding 12 months.
Aim
Application
The Act is applicable to all Railway employees, and person employed in industrial establishments, and others whose wages are less than Rs. 1600 per month.
Wages include
Wages does not include TA, bonus, housing accommodation, services and amenities provided, contribution paid by employer towards pension or gratuity, value of free passes and PTOs, value of rent free quarters, value of medical attendance, subsistence allowance etc.
Wages responsibility of Payment of Wages
Wage Period
Employer is responsible to fix the wage period for arranging payment and in no case the wage period shall exceed one month.
Payment Day
Where there are less than 1000 employees, the wages should be paid before the expiry of the 7th day after the wage period. Where there are 1000 or more employees, the wages should be paid before the expiry of the 10th day after the last day of the wage period.
If the employer terminates the employment, the wages earned should be paid before the expiry of the second working day from the date of termination.
Authorised Deductions
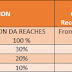
Wages of an employee should be paid without deduction except those authorized under the act. Deductions should not exceed 75% of wages, if deductions towards cooperative / consumer society are made and it should not exceed 50% of wages in other cases.
The authorized deductions are :
Notices
The inspector of Factories, labour Inspectors and CIRM officials functions as Inspectors under the Act.
Penalties
Penalties are prescribed for omissions like failure of payment/delayed payment/unauthorized deductions and failure to display notices/registers.
Source: http://indianrailwayemployee.com/content/payment-wages-act-1936
The payment of Wages Act, 1936 is an important piece of legislation which regulates the payment of wages to employees in the industrial and other establishments, who are in respect of wages with average upto Rs.1600/- per month. It seeks to ensure timely payment of wages without any unauthorised deductions.
The payment of wages (Railways) Rules, 1936, as amended from time to time, were framed by the Central Government to secure proper enforcement of the provisions of the Payment Of Wages Act in respect of persons employed in railway including railway contractors who employ 20 or more persons on any day in the preceding 12 months.
Aim
- To secure regular, prompt and cash payment
- To fix wage period
- To regulate the deductions made from the wages
Application
The Act is applicable to all Railway employees, and person employed in industrial establishments, and others whose wages are less than Rs. 1600 per month.
Wages include
- Basic pay.
- Officiating allowance.
- Leave salary.
- Overtime allowance.
- Special Compensatory allowance.
- House Rent allowance.
- Increment.
- Payment in lieu of notice period.
- Payment for piecework.
- Running allowance etc.
Wages does not include TA, bonus, housing accommodation, services and amenities provided, contribution paid by employer towards pension or gratuity, value of free passes and PTOs, value of rent free quarters, value of medical attendance, subsistence allowance etc.
Wages responsibility of Payment of Wages
- The employer is responsible for the payment of wages to persons employed by him.
- Payment of wages should be made on a working day.
- Payment of wages should be in coins or currency in vogue.
- Payment in kind is not permissible.
Wage Period
Employer is responsible to fix the wage period for arranging payment and in no case the wage period shall exceed one month.
Payment Day
Where there are less than 1000 employees, the wages should be paid before the expiry of the 7th day after the wage period. Where there are 1000 or more employees, the wages should be paid before the expiry of the 10th day after the last day of the wage period.
If the employer terminates the employment, the wages earned should be paid before the expiry of the second working day from the date of termination.
Authorised Deductions
Wages of an employee should be paid without deduction except those authorized under the act. Deductions should not exceed 75% of wages, if deductions towards cooperative / consumer society are made and it should not exceed 50% of wages in other cases.
The authorized deductions are :
- Fines.
- Salary for absence from duty.
- Damage or loss of goods expressly entrusted to the employee or for loss of money for which the employee is accountable.
- Amenities and services.
- Income tax.
- Court attachments.
- Payment to cooperative societies.
- Insurance premium.
- House rent and allied charges.
- Loans and advances.
- Station and Stores debits.
- Prime Minister’s relief found.
- National defense fund.
Notices
- Number of persons employed.
- Wage period.
- Date of payment.
- Abstract of the Payment of Wages Act.
- Register
- Fines.
- Deductions
- Wages.
- Advances
- Inspectors
The inspector of Factories, labour Inspectors and CIRM officials functions as Inspectors under the Act.
Penalties
Penalties are prescribed for omissions like failure of payment/delayed payment/unauthorized deductions and failure to display notices/registers.
Source: http://indianrailwayemployee.com/content/payment-wages-act-1936





0 comments:
Post a Comment